All the parts of a diesel generator come together in a single machine to transform energy from one form to another. Essentially, a power generator works by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. The diesel engine supplies mechanical energy to the alternator, which then converts it into electrical power through the process of electromagnetic induction in a magnetic field. Understanding the key components of a diesel generator is crucial for maximizing its performance. Various suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors offer diesel generator parts, with several diesel generators available for sale on our website. Feel free to reach out to us for more information. Contrary to common belief, no actual electricity is produced. The operation of a single electric generator or multiple synchronous generators relies on Michael Faraday’s theory of electromagnetic induction, which we will discuss in this guide to diesel generator components.
Diesel Generators
Diesel generators provide either continuous or backup power to a variety of users, including homes, schools, hospitals, and industrial facilities. These generators come in various sizes, ranging from compact, portable models to larger units suitable for buildings. Each user can find an appropriate generator to meet their specific needs. By converting the energy from diesel fuel into electrical power, these generators supply electricity to connected devices or systems. Each diesel generator consists of at least nine key components that work together to produce electrical power. Below, we break down and explain each part. In the diagram, the main diesel generator components are labeled and numbered for easy identification.
Here are the 10 primary parts of a diesel generator:
- Diesel Engine
- Alternator
- Fuel System
- Voltage Regulator
- Cooling System and Exhaust System
- Lubrication System
- Battery Charger
- Control Panel
- Main Assembly Frame
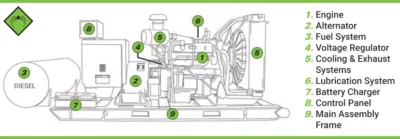
The main diesel generator parts (Reference: https://ade-power.com/)
Diesel Engine
The diesel engine serves as the source of mechanical energy in a generator. Its size plays a critical role, as it directly correlates with the amount of electrical energy the generator can produce. In other words, a larger engine is required to generate higher output power. The type of diesel engine used in generators is similar to those commonly found in cars, trucks, and large vehicles, known for their durability and efficiency in converting fuel into mechanical power.
Alternator
The alternator is the key component responsible for generating electrical power in a diesel generator. Its function is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The alternator contains several complex parts, with one of the most important being the rotor. The rotor consists of a shaft that spins, driven by the mechanical energy supplied by the diesel engine. Surrounding this shaft are multiple permanent magnets, which generate a magnetic field as they rotate.
This rotating magnetic field moves around another crucial component—the stator. The stator is made up of several electrical conductors tightly wound around an iron core. According to the principle of electromagnetic induction, when a magnetic field moves around a stationary conductor, it induces an electrical current.
Fuel System
The fuel system in a diesel generator typically includes a fuel tank connected to the engine by a pipe, allowing diesel to be supplied directly to the engine to initiate power generation. The size of the fuel tank determines how long the generator can operate continuously. Many silent canopy generators come standard with fuel tanks integrated into the base of the generator. If a larger fuel capacity is needed, a custom-designed extended base fuel system or an additional standalone bulk fuel tank can be used.
Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator is one of the most intricate components of a diesel generator. Its primary function is to ensure the generator produces a stable and consistent voltage output. While the internal workings of the voltage regulator are complex, the main purpose is to regulate the voltage, preventing fluctuations caused by variations in engine speed.
Without a voltage regulator, significant voltage swings would occur, making it difficult for electrical devices to function properly. These fluctuations could lead to damage or malfunction in connected equipment.
Cooling and Exhaust System
Both the cooling system and the exhaust system play crucial roles in the operation of a diesel generator.
The cooling system is responsible for preventing the generator from overheating. It works by circulating coolant inside the generator to absorb excess heat produced by the engine and alternator. The heated coolant then flows through a heat exchanger, where the heat is released and expelled from the generator.
The exhaust system functions similarly to a car’s exhaust system. It captures the gases generated by the combustion process in the diesel engine and channels them through a piping system, safely venting them away from the generator to prevent harmful buildup within the unit.
Lubrication System
The lubrication system is essential for keeping the diesel generator’s engine running smoothly. It pumps oil into the engine to ensure that all moving parts are properly lubricated, preventing them from grinding against each other and reducing friction. Without an efficient lubrication system, the engine would experience excessive wear and eventually break down due to overheating and mechanical damage. Proper lubrication is key to extending the lifespan of the generator and ensuring its reliable operation.
Battery Charger
A diesel engine relies on a small electric motor, known as a starter motor, to initiate its operation. This motor works in conjunction with a battery, which provides the power needed to start the engine. The battery itself needs to be regularly charged to ensure the generator can start whenever required, which is where the battery charger comes into play. This component ensures the battery stays charged and ready to supply power to the starter motor when needed.
Control Panel
The control panel is the central hub for operating and managing the diesel generator. It includes various control features such as the start button, frequency switch, engine fuel indicator, coolant temperature gauge, and more, allowing the user to perform multiple tasks and monitor key functions.
The control panel handles the start and stop processes of the generator, while also monitoring the engine and alternator to ensure proper operation. It plays a critical role in overseeing the generator’s performance, providing maintenance alerts, and managing control functions. Additionally, the control panel can synchronize multiple generators for parallel operation when needed, ensuring smooth and efficient power delivery.
Main Assembly Frame
The main assembly frame is essential for holding the entire generator together. It provides the structure that houses all the diesel generator components, ensuring they are securely mounted and properly aligned.
The frame can either be open or closed (canopied), depending on the design. A canopied frame offers extra protection and sound attenuation, reducing noise during operation. Outdoor generators are typically housed in weatherproof frames, protecting the generator from environmental damage and ensuring durability in various conditions. The main assembly frame not only offers structural support but also helps shield the generator from external elements.
Now that you’re familiar with how a diesel generator operates and its key components, here’s a brief recap: The diesel engine generates mechanical energy, which is transferred to the alternator. The alternator then converts this mechanical energy into electrical power through electromagnetic induction in the presence of a magnetic field. This process enables the generator to supply electrical energy for various applications.
Contact LexiGen Power Solutions Limited for all your diesel generator and spare parts requirements.








